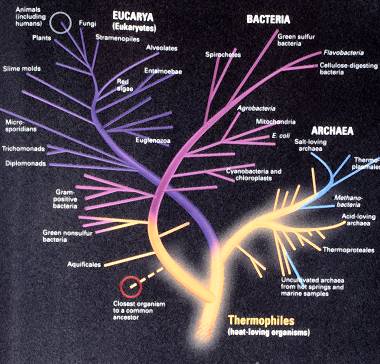
This is a fine tree of life. The small letters are hardly readable but
that is not important. The first living organisms must have come into existence
in a very hot environment: the yellow base of the tree. The first branch
on the left-hand side is the one of the bacteria. The first
cyanobacteria with photosynthesis (the capacity to make starch out of
carbondioxide and water) appeared at the border of warm and cold.
The first branch on the right-hand side goes to the
Archaea. These prokaryotes obtain their energy, among others,
from sulphur.
The second branch on the left-hand side represents the Eukaryotes, the organisms
with cells with a nucleus. Multicellular organisms like plants and animals
are also included. The animals (man inclusive) are mentioned on the top left
inside a small circle.
Know more?
Three-domain
system |
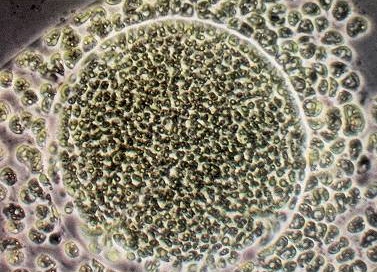
This is a photo of a part of a (living) primitive organism called
Volvox. It is a green alga consisting of cells which are mutually
connected by strands of protoplasm, and which have arranged themselves on
the surface of a sphere. The organism, sized up to 1 mm and living in
freshwater ditches and pools, can be considered on the other hand as a colony
of cooperating algal cells. Every cell has two flagella which can be used
to rotate and to move the sphere. The cells are not yet specialized
and it is imaginable that transitional forms from one-celled to multicellular
organisms had a comparable structure.
From time to time new little spheres are formed within the old one (photo)
and at a certain moment these new spheres go outward and get detached. This
is a kind of vegetative propagation. However, there is also a sexual
reproduction.
Know more?
Volvox (3D-photos: red-green spectacles needed)
|