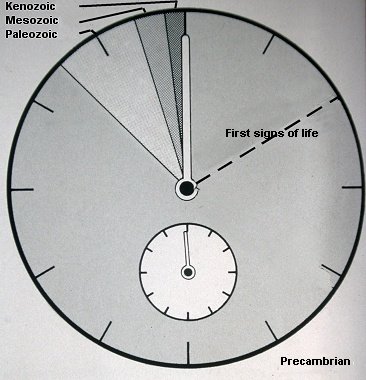
| The age of the Earth is about 4.6 billion years. In the image above those
4.6 billion years is depicted as a 12 hours clock. The first signs of life
are fossil cyanobacteria (single-celled organisms without a nucleus). Their
age is between 3.8 and 3.5 billion years (that means at about 2 o'clock).
During the entire Precambrian, which lasted till 543 million years ago, the
cyanobacteria were the most common life form. About 2 billion years ago (at
5.35) cells with a nucleus came into being, the Eukaryotes, and only by the
end of the Precambrian (at 10.18) the first multicellular organisms occurred.
At the beginning of the Paleozoic (at 10.20) an enormous outburst of life
forms must have happened for from that moment on the sediments are full of
fossils. The Paleozoic ends (at 11.35) with a disastrous extinction at the
end of the Permian, 250 million years ago. Then the Mesozoic starts, the
period of the dinosaurs. It ends with a great extinction at the end of the
Cretaceous, 65 million years ago (at 11.50). One of the causes was probably
the impact of a huge meteorite. Next begins the Cenozoic, in which period
we still live now. Modern man came into existence about one second and a
half before twelve. And we are now the cause of a large extinction ...
Know more?
Cyanobacteria |
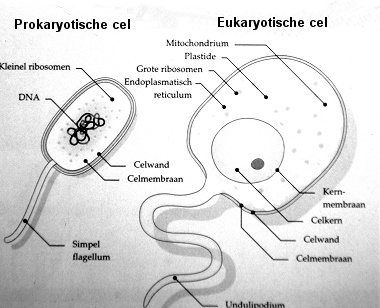
The cyanobacteria were prokaryote, that means that they
were single-celled and without a nucleus. Their hereditary material was floating
loose in the cell. Cyanobacteria could produce food from carbon dioxide and
water and they brought oxygen in the atmosphere. Until about 1.8 billion
years ago this oxygen was absorbed by free iron in the seas and fixed in
thick layers of iron compound. Only thereafter gradually free oxygen came
into the atmosphere.
Around 2 billion years ago the eukaryotes came into being:
single-celled organisms with a nucleus and different kinds of organelles
(very small organs). The chromosomes were situated in the nucleus. Probably
dents from the surface have formed a protection around the DNA molecules
and this structure has evolved into a nucleus. Several kinds of organelles
seem to have been prokaryotes living inside another cell. This was a kind
of symbiosis, in this case called endosymbiosis. An important
indication for this is the fact that the mitochondria (the energy factories
in the cell) have their own DNA. Some of the eukaryotes have a flagellum
as well. It is not impossible that this flagellum is also the result of a
symbiosis with a prokaryote. Eukaryotes are much more complicated than
prokaryotes. They came into existence by a kind of evolution which is totally
different from the type discussed before with mutations and variations. But
surely natural selection will have played an important role.
Know more?
From Prokaryotes to Eukaryotes
|