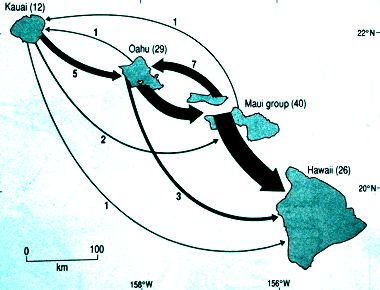
In the past some fruit flies were probably blown over to the Hawaiin
archipelago. This island group lies far from the continent and therefore
has a species-poor fauna. That is the reason that many
niches (area's in which an organism is able to live) are not
occupied by animals. From the few firstcomers hundreds of new species have
evolved. This was possible because very few insects were living on the Hawaiin
Islands. Thus species of fruit flies resembling beetles have developed, because
there were no beetles on the islands. Some of the descendants of the fruit
flies are as large as 2.5 cm! On the little map above is visualised
how many species occur on each of the islands and how many times a couple
of flies have crossed the sea to another island to become founder of a new
species.
It is called the founder effect when from a very small number
of individuals a new species comes into existence. If the 'founder' had some
special characteristic, then the trait will be preserved in the gene pool.
Example: In the USA exists an Indian village with relatively many albinos.
That is a consequence of the fact that the founders were albino's.
Know more?
Fruit
flies on Hawaii
Founder
effect |
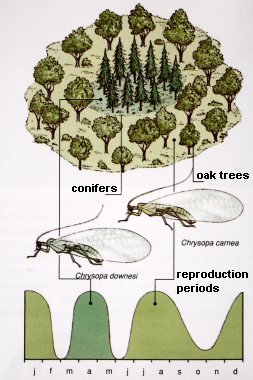
Besides allopatric speciation there is also sympatric
speciation. This is the formation of new species in the same area
as the original species. This is e.g. possible when a population changes
to another kind of food, or when it changes the breeding season. This model
is much less common than the allopatric one, but in small animals like insects
it is not rare. The example in the figure above is about insects which happen
to come in a different food tree and adapt to that one. When the new tree
produces the food at a different moment, the insects will change there life
cycle giving the larvae the best possible chance to develop. In this way
a difference in breeding time comes into being between the new and the old
population, with the consequence that gene exchange stops. Now there is a
new species. If you want, you can see this also as allopatric speciation,
because a kind of geographic barrier (two different tree species) has come
into existence for the insects.
Know more?
Allopatric speciation
Sympatric speciation |