After Patterson: Evolutie (1981)
After Patterson: Evolutie (1981)
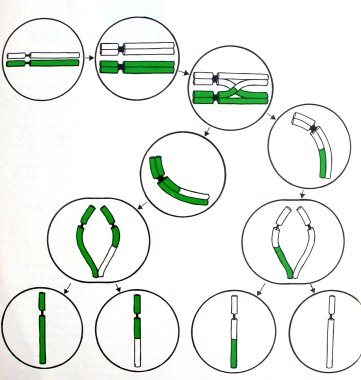
However, the cards are still more shuffled because often 'crossing-over' is taking place in the formation of the reproductive cells. During the so-called reduction division (also meiosis: see diagram) parts of the chromatides, originating from the father and the mother, are exchanged. As a consequence traits of the father as well as from the mother occur often in the same chromosome.
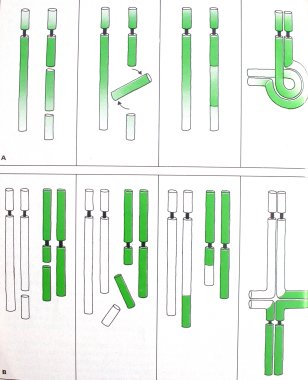
On top are some examples of mutations: a part of a chromosome can get detached and fill in the gap in the opposite direction.
And: a part of a chromosome can change place with a (longer) part of a second chromosome.
The most common mutation is the so-called point mutation in which the chromosome is changed in only one point.
Know more?
Mutations