After Pope: Het raadsel van het leven (1986)

After De Beer:Atlas van de evolutie (1966)
A chromosome consists of two coiled strings, called chromatids. One gene consists of two alleles, one on each chromatid. These alleles may be different, though they are part of the same gene. Think of the long pea (A) and the short one (a) of Mendel. A and a are alleles of the length gene of the pea plant.
During the formation of the reproductive cells the chromatids diverge and in the end each reproductive cell contains such a single string. When an egg-cell and a sperm-cell fuse, a complete chromosome comes again into existence.
Know more?
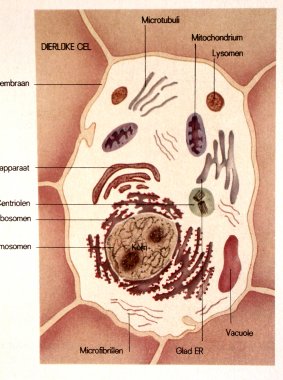
Cell
structure