
After Skelton: Evolution (1993)
Mendel discovered his heredity laws doing experiments with the growing of pea races.
Know more?
Gregor
Mendel
Biography
of Hugo de Vries
Evolution 8 |
|
|
| Evolution is strongly connected with genetics. The founder of the
theory of heredity is the Czech monk Gregor Mendel (1822 - 1884), a contemporary
of Darwin. He published his results in 1865, but time was apparently not
yet ripe, for no attention was paid to his publication. Only around 1900
his work was rediscovered, among others by the Dutchman Hugo de Vries. Mendel discovered his heredity laws doing experiments with the growing of pea races.
Know more? |
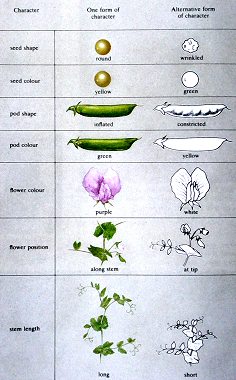
He cross fertilized races which differed in all sorts of traits, like surface and colour of the peas, shape and colour of the legumes, colour of the flowers, place of the inflorescences and the height of the plant. He discovered that the hereditary traits are 'hard' in many cases, i.e. that they don't mix, as was commonly thought in the time. For example, if you cross fertilize long and short plants, you will get as a result again long and short plants and not intermediate ones. (For that matter, this occurs too but Mendel had the fortune not to come across these cases in his experiments). Besides he found out that some of the characteristics are dominant and others recessive. The meaning of this will be explained hereafter. |
Evolution 8 |