
In 1876 his book on the effects of cross-pollination and self-pollination in plants came out. The subject had long occupied Darwin's mind because of the chance of inbreeding in his family as a consequence of the many marriages between the Darwins and the Wedgwoods. Darwin has always been afraid for hereditary illnesses in his children. There was not enough cross-pollination in his family, so to say.
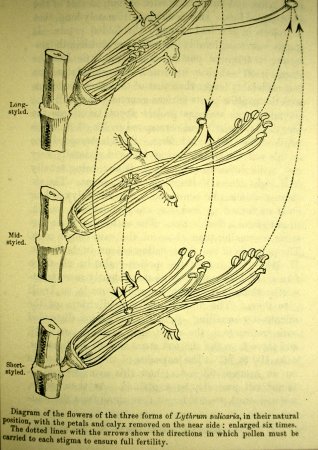
Plants have developed all kinds of methods to prevent self-pollination. This was the subject of his book on different forms of flowers in plants of the same species. For example the Lythrum or Cat-tail (see both pictures above; the left one from Darwin's book).
- Type 1: with long styles and half-long and short stamens
- Type 2: with half-long styles and short and long stamens
- Type 3: with short styles and half-long and long stamens.
At home Darwin grew a huge quantity of cat-tails at home and with the help of his son Francis he performed 223 pollinations in all 18 possible combinations. The flowers were castrated and with a small brush the fertilization was effected. Thereafter they noted when the seeds were ripe and then they collected and counted the seeds. The next step was to disseminate them, etc.
The result was as Darwin already expected: long-styled flowers must be pollinated by pollen from long stamens, half-long-styled flowers by pollen from half-long stamens and short ones by short ones. Other combinations gave also some seeds but much less. Conclusion: this is a way to stimulate cross-pollination. The fact that self-fertilization also yields seeds can be useful in the case that a plant is growing alone somewhere.
This is a nice example of Darwin's clear way of thinking and experimenting.